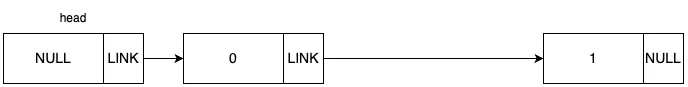
LinkedList?
LinkedList(연결 리스트)는 이름 그대로 데이터를 저장할 때 다음 데이터의 위치도 함께 저장해서 연결하는 형식으로 데이터를 저장하는 자료구조입니다. 노드끼리 연결한 형태로 구성된 연결 리스트 특성상 데이터를 추가할 때 배열처럼 연속적인 공간 할당이 필요하지 않습니다. 그래서 연결 리스트는 메모리 공간 압박에서 좀더 자유로우며, 데이터 추가/삭제 속도도 배열보다 빠릅니다.
하지만 단점도 있습니다. 연결 리스트는 데이터가 연속된 메모리 공간에 저장되어 있지 않아서 데이터를 가져올 때 첫 노드부터 순차적으로 탐색해야 합니다. 하지만 배열은 데이터가 연속적인 메모리 공간에 저장되므로 원하는 인덱스의 값을 바로 가져올 수 있습니다.
그래서 데이터 추가/삭제 작업이 빈번하게 발생할 때는 연결 리스트, 데이터를 가져오는 작업이 빈번하게 발생할 때는 배열을 사용합니다.
동작 원리
연결 리스트는 기본적으로 노드로 구성됩니다. 한 노드에는 데이터와 다음 노드의 주소값을 저장합니다.
연결 리스트를 구성할 땐 맨 앞에 head 노드를 두고, head 노드부터 노드를 추가해 나가는 방식으로 구현됩니다. 자세한 구현 방법은 코드를 보며 설명하겠습니다.
구조체 선언
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
typedef struct node {
int data; // 데이터 저장
struct node *next; // 다음 노드 주소값 저장
} Node;
typedef struct {
Node *head; // LinkedList의 가장 첫 노드
size_t size; // LinkedList의 길이
} LinkedList;
Node 구조체는 연결 리스트의 노드를 구현한 구조체 입니다. 데이터 저장을 위한 data 변수와 다음 노드의 주소값 저장을 위한 node 구조체의 포인터 변수로 구성되어 있습니다.
LinkedList 구조체는 리스트의 가장 첫 노드인 head 노드의 주소값 저정을 위한 포인터 변수와, 리스트의 길이를 나타내기 위한 size 변수로 구성됩니다.
데이터 삽입
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
void insertData(LinkedList *list, int index, int value) {
// 타겟 idx 크기가 현재 리스트 길이보다 길다면 함수 종료
if (index > list->size) return;
// head 노드로 타겟 초기화
Node *target = list->head;
for (int i = 0;i < index;i++) {
// 타겟 idx의 노드 가져옴
target = target->next;
}
// 추가할 새 노드 할당
Node *newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
// 새 노드의 데이터 업데이트
newNode->data = value;
// 새 노드의 다음 노드 = 타겟 노드의 다음 노드
newNode->next = target->next;
// 타겟 노드의 다음 노드 = 새 노드
target->next = newNode;
// 리스트 사이즈 + 1
list->size++;
}
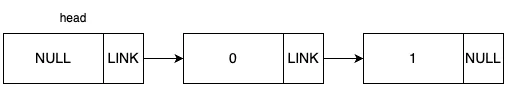
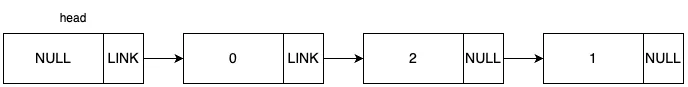
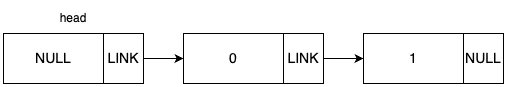
원하는 위치와 데이터를 입력 받아서 값을 추가하는 함수 입니다. 전체적인 동작 과정을 그림으로 표현하면 다음과 같습니다.
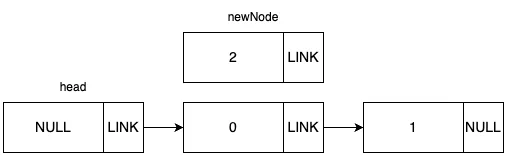
초기 그래프가 위 그림과 같은 상태일 때, 데이터 2를 1번 idx에 추가하는 상황을 예로 들겠습니다.
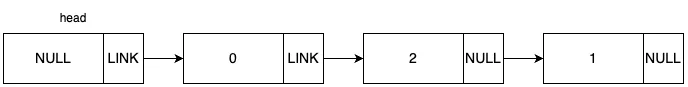
우선 새 노드를 할당 후, 데이터 2를 노드에 넣습니다.
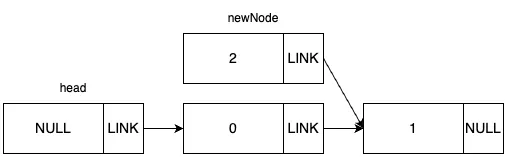
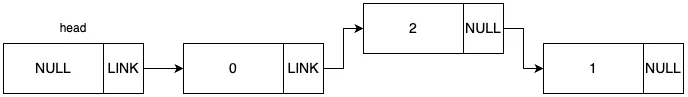
새 노드의 다음 노드 값을 들어갈 자리에 있는 노드의 다음 노드로 지정합니다.
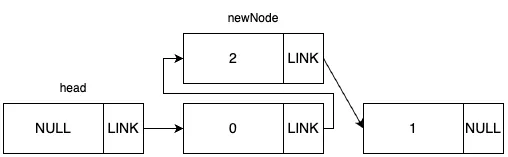
들어갈 자리에 있는 노드의 다음 노드를 새 노드로 지정합니다.
결과적으로 새 노드는 1번 idx에 들어가게 되었습니다.
데이터 삭제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
void removeData(LinkedList *list, int index) {
// 타겟 idx 크기가 현재 리스트 길이보다 길다면 함수 종료
if (index >= list->size) return;
// head 노드로 타겟 초기화
Node *targetPrev = list->head;
for (int i = 0;i < index;i++) {
// 삭제할 타겟 노드의 이전 노드 가져옴
targetPrev = targetPrev->next;
}
// 타겟 노드 가져옴
Node *target = targetPrev->next;
// 타겟 노드의 다음 노드 가져옴
Node *targetNext = target->next;
// 타겟 노드의 이전 노드의 다음 노드 = 타겟 노드의 다음 노드
targetPrev->next = targetNext;
// 타겟 노드 삭제
free(target);
// 리스트 사이즈 - 1
list->size--;
}
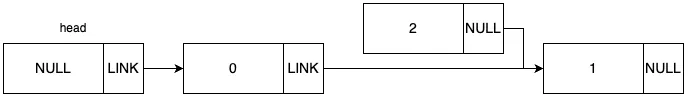
원하는 위치를 입력 받아서 값을 삭제하는 함수 입니다. 전체적인 동작 과정을 그림으로 표현하면 다음과 같습니다.
초기 그래프가 위 그림과 같은 상태일 때, 1번 idx에 삭제하는 상황을 예로 들겠습니다.
우선 타겟 노드인 1번 노드와 그 앞 뒤 노드를 모두 가져옵니다.
타겟 노드의 이전 노드의 다음 노드를 타겟 노드의 다음 노드로 지정합니다.
타겟 노드를 삭제합니다.
결과적으로 1번 노드는 삭제되고, 1번 노드의 앞 뒤 노드가 이어지게 되었습니다.
전체 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
} Node;
typedef struct {
Node *head;
size_t size;
} LinkedList;
void insertData(LinkedList *list, int index, int value) {
if (index > list->size) return;
Node *target = list->head;
for (int i = 0;i < index;i++) {
target = target->next;
}
Node *newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = target->next;
target->next = newNode;
list->size++;
}
void removeData(LinkedList *list, int index) {
if (index >= list->size) return;
Node *targetPrev = list->head;
for (int i = 0;i < index;i++) {
targetPrev = targetPrev->next;
}
Node *target = targetPrev->next;
Node *targetNext = target->next;
targetPrev->next = targetNext;
free(target);
list->size--;
}
void printList(LinkedList *list) {
Node *currentNode = list->head->next;
while (currentNode != NULL) {
printf("%d ", currentNode->data);
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void freeList(LinkedList *list) {
Node *nextNode = list->head;
while (nextNode != NULL) {
Node *tmp = nextNode->next;
free(nextNode);
nextNode = tmp;
}
}
int main() {
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->next = NULL;
LinkedList list;
list.head = head;
list.size = 0;
char command[10];
int number;
size_t index;
printf("Commands: insert <index> <num>, del <index>, print, exit\n");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%s", command);
if (strcmp(command, "insert") == 0) {
scanf("%zu %d", &index, &number);
insertData(&list, index, number);
} else if (strcmp(command, "del") == 0) {
scanf("%zu", &index);
removeData(&list, index);
} else if (strcmp(command, "print") == 0) {
printList(&list);
} else if (strcmp(command, "exit") == 0) {
break;
} else {
printf("Invalid command.\n");
}
}
freeList(&list);
return 0;
}