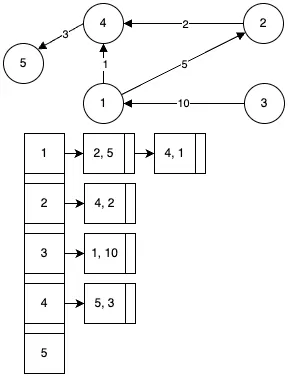
Graph?
그래프는 연결된 객체간의 관계를 표현하는데 사용하는 자료구조입니다. 객체간의 관계를 표현할 수 있기 때문에 사회 네트워크, 도로망, 인터넷 등 실생활의 다양한 요소를 표현할 수 있습니다.
용어 정리
우선 그래프에서 쓰이는 용어 먼저 정리하겠습니다.
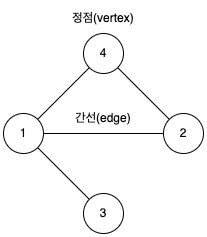
- 정점(Vertex, V): 데이터가 저장되는 그래프의 기본요소 입니다. 노드(Node)라고도 불립니다.
- 간선(Edge, E): 두 정점을 연결하는 선으로, 그래프의 구조를 형성합니다. 링크(Link)라고도 불립니다. 그래프의 종류에 따라 방향, 가중치를 가질 수 있습니다. 이 부분은 뒤에서 자세히 설명하겠습니다.
- 차수(Degree): 한 정점에 연결된 간선의 수 입니다. 방향 그래프에서는 진입 차수(In-Degree)와 진출 차수(Our-Degree)로 세분화 됩니다.
- 인접 정점(Adjacency Vertex): 두 정점이 간선으로 직접 연결된 경우, 이 두 정점은 인접해 있다고 합니다.
- 경로(Path): 한 정점에서 다른 정점으로 이동하는 길을 뜻합니다. 정점 이동 과정 중 거쳐가는 정점들을 나열해서 표현합니다.
- 사이클(Cycle): 시작과 종료 지점이 동일한 경로를 뜻합니다. 적어도 하나 이상의 간선을 포함합니다. 무방향 그래프에서는 어떠한 정점도 두 번 이상 방문하지 않고 시작과 종료 지점이 같은 경로입니다.
그래프 유형
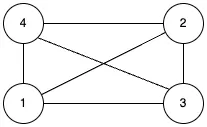
무방향 그래프
간선에 방향이 없는 그래프입니다. 연결된 두 정점은 양방향으로 자유롭게 이동이 가능합니다. 위 그래프에서 1과 4의 간선을 (1, 4), (4, 1)로 표현합니다.
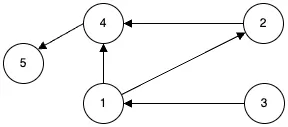
방향 그래프
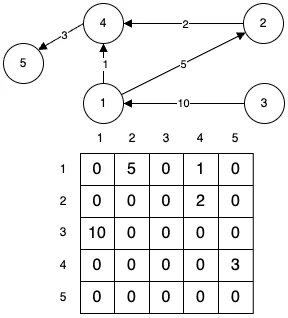
간선에 방향이 있는 그래프입니다. 두 정점간의 이동은 항상 간선의 방향으로만 가능합니다. 위 그래프에서 1과 4의 간선을 <1, 4>로 표현합니다.
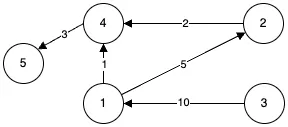
가중치 그래프
간선에 가중치가 부여된 그래프입니다. 가중치는 거리, 시간, 비용 등 다양한 형태를 표현 가능합니다.
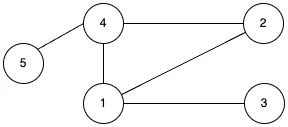
완전 그래프
모든 정점 쌍 사이에 하나의 간선이 존재하는 그래프 입니다.
이 외에도 순환 그래프, 비연결 그래프 등 다양한 그래프가 있습니다.
표현 방식
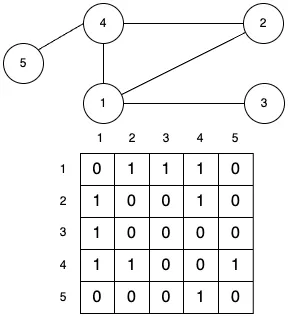
그래프는 주로 인접 행렬(Adjacency Matrix)과 인접 리스트(Adjacency List)로 표현됩니다.
인접 행렬(Adjacency Matrix)
그래프의 정점들 간의 연결 관계를 행렬로 표현한 형태입니다. 주로 2차원 배열을 이용해 표현됩니다.
특징
- 정점이 N개라면 인접행렬도 \(N \times N\) 크기입니다.
- 정점 i, j 사이에 간선이 존재한다면 인접행렬 i, j에 숫자 1 또는 가중치 값이 들어갑니다.
- 무방향 그래프라면 행렬 i, j와 j, i에 동일한 값으로 표현됩니다. 그래서 무방향 그래프의 인접행렬은 대칭입니다.
- 방향 그래프는 간선 i, j는 행렬 i, j에만 표현됩니다.
- 두 정점 간 간선이 존재하지 않는다면 0 또는 무한대의 값이 들어갑니다.
장점
- 특정 정점 i와 j간의 간선 유무를 \(O(1)\) 만에 확인이 가능합니다.
- 구현이 단순합니다.
단점
- 공간복잡도가 \(O(n^2)\)으로 공간 낭비가 심합니다. 간선 수에 비해 지나치게 많은 공간을 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 모든 간선의 수를 알아내려면 모든 인접행렬을 확인해야 하므로 \(O(n^2)\)의 시간이 소요됩니다.
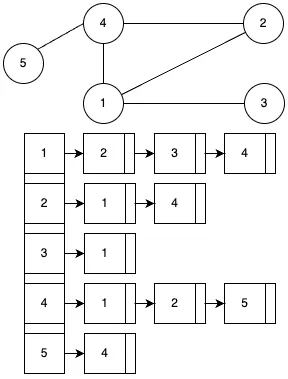
인접 리스트(Adjacency List)
각 정점에서 출발하는 간선의 목록을 배열 또는 연결리스트로 저장하여 그래프를 표현하는 형식입니다.
특징
- 각 요소가 하나의 정점을 표현합니다.
- 각 요소는 해당 정점에서 출발해서 도달할 수 있는 정점의 번호가 기록됩니다.
- 무방향 그래프라면 간선 i, j는 i 요소에는 j를, j 요소에는 i를 추가해야 합니다.
- 가중치 그래프라면 요소에 정보를 추가할 때 (정점 번호, 가중치) 로 표현하여 넣기도 합니다.
장점
- 공간복잡도가 \(O(V + E)\)로, 사용하는 메모리가 실제 간선 수에 비례합니다.
단점
- 특정 두 정점간의 연결을 확인하기 위해서는 정점의 모든 인접 리스트를 탐색해야 하므로 정점의 차수 만큼의 시간이 필요합니다.
- 인접 행렬에 비해 구현이 어렵습니다.
동작 원리
인접 행렬과 인접 리스트로 나누어 각각 설명하겠습니다. 무방향 그래프를 생성하고 간선을 추가/삭제하는 예제입니다.
인접 행렬
구조체 선언
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
typedef struct {
// 정점 개수
int nodeCount;
// 인접 행렬
int matrix[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
} Graph;
Graph initGraph() {
Graph graph;
// 정점 개수 0
graph.nodeCount = 0;
// 인접 행렬 모두 0
for (int i = 0;i < MAX_SIZE;i++) {
for (int j = 0;j < MAX_SIZE;j++) {
graph.matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return graph;
}
Graph 구조체는 정점의 개수를 저장하는 nodeCount, 간선 정보를 저장하는 matrix로 구성됩니다. 그래프 초기화시 정점 개수는 0, 인접 행렬은 모두 0으로 초기화 합니다.
정점 추가
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
void addVertex(Graph *graph) {
// 이미 최대 개수만큼 정점 있으면 함수 종료
if (graph->nodeCount == MAX_SIZE) return;
// 정점 개수 + 1
graph->nodeCount++;
// 추가되는 정점과 다른 정점간의 관계 초기화
for (int i = 0;i < graph->nodeCount;i++) {
graph->matrix[graph->nodeCount - 1][i] = 0;
graph->matrix[i][graph->nodeCount - 1] = 0;
}
}
정점을 추가하는 함수입니다. 추가되는 정점과 다른 정점간의 관계를 모두 0으로 바꾸어 초기화 해줍니다.
간선 추가
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
void addEdge(Graph *graph, int start, int end) {
// 시작/끝 정점이 범위 밖이면 함수 종료
if (start < 0 || start >= graph->nodeCount
|| end < 0 || end >= graph->nodeCount) return;
// 무방향 그래프 이므로 양쪽 모두 인접 행렬 1로 표현
graph->matrix[start][end] = 1;
graph->matrix[end][start] = 1;
}
간선 정보를 추가하는 함수입니다. 예제는 무방향 그래프 이므로 좌, 우 정점 번호를 받아 양방향으로 업데이트 합니다.
간선 삭제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
void removeEdge(Graph *graph, int start, int end) {
// 시작/끝 정점이 범위 밖이면 함수 종료
if (start < 0 || start >= graph->nodeCount
|| end < 0 || end >= graph->nodeCount) return;
// 무방향 그래프 이므로 양쪽 모두 간선 정보 삭제
graph->matrix[start][end] = 0;
graph->matrix[end][start] = 0;
}
간선 정보를 삭제하는 함수입니다. 예제는 무방향 그래프 이므로 좌, 우 정점 번호를 받아 양방향 모두 삭제합니다.
전체 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 50
typedef struct {
int nodeCount;
int matrix[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
} Graph;
Graph initGraph() {
Graph graph;
graph.nodeCount = 0;
for (int i = 0;i < MAX_SIZE;i++) {
for (int j = 0;j < MAX_SIZE;j++) {
graph.matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return graph;
}
void addVertex(Graph *graph) {
if (graph->nodeCount == MAX_SIZE) return;
graph->nodeCount++;
for (int i = 0;i < graph->nodeCount;i++) {
graph->matrix[graph->nodeCount - 1][i] = 0;
graph->matrix[i][graph->nodeCount - 1] = 0;
}
}
void addEdge(Graph *graph, int start, int end) {
if (start < 0 || start >= graph->nodeCount
|| end < 0 || end >= graph->nodeCount) return;
graph->matrix[start][end] = 1;
graph->matrix[end][start] = 1;
}
void removeEdge(Graph *graph, int start, int end) {
if (start < 0 || start >= graph->nodeCount
|| end < 0 || end >= graph->nodeCount) return;
graph->matrix[start][end] = 0;
graph->matrix[end][start] = 0;
}
void printGraph(Graph *graph) {
for (int i = 0; i < graph->nodeCount; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < graph->nodeCount; j++) {
printf("%d ", graph->matrix[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main() {
Graph graph = initGraph();
int v = 0;
printf("정점 개수: ");
scanf("%d", &v);
for (int i = 0;i < v;i++) {
addVertex(&graph);
}
char command[10];
int num1, num2;
printf("Commands: insert <vertex1> <vertex2>, del <vertex1> <vertex2>, exit\n");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%s", command);
if (strcmp(command, "insert") == 0) {
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
addEdge(&graph, num1, num2);
printGraph(&graph);
} else if (strcmp(command, "del") == 0) {
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
removeEdge(&graph, num1, num2);
printGraph(&graph);
} else if (strcmp(command, "exit") == 0) {
break;
} else {
printf("Invalid command.\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
인접 리스트
구조체 선언
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
typedef struct node {
// 이어진 정점 번호
int vertex;
// 다음 연결리스트 노드 주소
struct node* next;
} Node;
typedef struct {
// 전체 정점 개수
int nodeCount;
// 간선 정보
Node** adjList;
} Graph;
Graph* initGraph() {
Graph *graph = (Graph*)malloc(sizeof(Graph));
graph->nodeCount = 0;
return graph;
}
Node 구조체는 인접리스트를 연결리스트로 구성하는 노드입니다. 이어진 정점을 저장하는 vertex, 다음 노드를 가르키는 포인터 변수 next로 구성되어 있습니다. Graph 구조체는 정점의 개수를 저장하는 nodeCount, 간선 정보를 저장하는 adjList로 구성됩니다. 그래프 초기화시 정점 개수는 0으로 초기화 합니다.
정점 추가
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
void addVertex(Graph* graph) {
// 정점 개수 + 1
graph->nodeCount++;
// 추가된 개수 만큼 인접 리스트 개수 재할당
graph->adjList = realloc(graph->adjList, graph->nodeCount * sizeof(Node*));
// 새로 할당된 인접 리스트 NULL 초기화
graph->adjList[graph->nodeCount - 1] = NULL;
}
정점을 추가하는 함수입니다. 기존 정점 개수 + 1 만큼의 공간을 새로 할당하고, 새로 할당된 인접 리스트의 시작을 NULL로 초기화 합니다.
간선 추가
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
void addEdge(Graph* graph, int start, int end) {
// 시작/끝 정점이 범위 밖이면 함수 종료
if (start < 0 || start >= graph->nodeCount
|| end < 0 || end >= graph->nodeCount) return;
// 좌측 정점에 연결 정보 추가를 위한 노드 할당
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
// 연결된 노드 값
newNode->vertex = end;
// 좌측 정점 연결 정보 추가
newNode->next = graph->adjList[start];
graph->adjList[start] = newNode;
// 무방향 그래프이므로 우측도 동일하게 추가
newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->vertex = start;
newNode->next = graph->adjList[end];
graph->adjList[end] = newNode;
}
간선 정보를 추가하는 함수입니다. 예제는 무방향 그래프 이므로 좌, 우 정점 번호를 받아 양방향으로 업데이트 합니다. 인접 리스트를 업데이트 하는 방식이 이해가 안가신다면 [자료구조] C로 LinkedList 만들기를 참고하시면 됩니다.
간선 삭제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
void removeEdge(Graph* graph, int start, int end) {
// 시작/끝 정점이 범위 밖이면 함수 종료
if (start < 0 || start >= graph->nodeCount
|| end < 0 || end >= graph->nodeCount) return;
// start 정점에 end 정점 값이 있는 노드를 찾아 제거
Node** pNode = &graph->adjList[start];
while (*pNode) {
Node* current = *pNode;
if (current->vertex == end) {
*pNode = current->next;
free(current);
break;
}
pNode = ¤t->next;
}
// end 정점에 start 정점 값이 있는 노드를 찾아 제거
pNode = &graph->adjList[end];
while (*pNode) {
Node* current = *pNode;
if (current->vertex == start) {
*pNode = current->next;
free(current);
break;
}
pNode = ¤t->next;
}
}
간선 정보를 삭제하는 함수입니다. 예제는 무방향 그래프 이므로 좌, 우 정점 번호를 받아 양방향 모두 삭제합니다.
전체 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct node {
int vertex;
struct node* next;
} Node;
typedef struct {
int nodeCount;
Node** adjList;
} Graph;
Graph* initGraph() {
Graph *graph = (Graph*)malloc(sizeof(Graph));
graph->nodeCount = 0;
return graph;
}
void addVertex(Graph* graph) {
graph->nodeCount++;
graph->adjList = realloc(graph->adjList, graph->nodeCount * sizeof(Node*));
graph->adjList[graph->nodeCount - 1] = NULL;
}
void addEdge(Graph* graph, int start, int end) {
if (start < 0 || start >= graph->nodeCount
|| end < 0 || end >= graph->nodeCount) return;
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->vertex = end;
newNode->next = graph->adjList[start];
graph->adjList[start] = newNode;
newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->vertex = start;
newNode->next = graph->adjList[end];
graph->adjList[end] = newNode;
}
void removeEdge(Graph* graph, int start, int end) {
if (start < 0 || start >= graph->nodeCount
|| end < 0 || end >= graph->nodeCount) return;
Node** pNode = &graph->adjList[start];
while (*pNode) {
Node* current = *pNode;
if (current->vertex == end) {
*pNode = current->next;
free(current);
break;
}
pNode = ¤t->next;
}
pNode = &graph->adjList[end];
while (*pNode) {
Node* current = *pNode;
if (current->vertex == start) {
*pNode = current->next;
free(current);
break;
}
pNode = ¤t->next;
}
}
void printGraph(Graph* graph) {
for (int i = 0; i < graph->nodeCount; i++) {
Node* temp = graph->adjList[i];
printf("Adjacency list of vertex %d:\n head", i);
while (temp) {
printf(" -> %d", temp->vertex);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void freeGraph(Graph* graph) {
for (int i = 0; i < graph->nodeCount; i++) {
Node* node = graph->adjList[i];
while (node) {
Node* temp = node;
node = node->next;
free(temp);
}
}
free(graph->adjList);
free(graph);
}
int main() {
Graph* graph = initGraph();
int v = 0;
printf("정점 개수: ");
scanf("%d", &v);
for (int i = 0;i < v;i++) {
addVertex(graph);
}
char command[10];
int num1, num2;
printf("Commands: insert <vertex1> <vertex2>, del <vertex1> <vertex2>, exit\n");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%s", command);
if (strcmp(command, "insert") == 0) {
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
addEdge(graph, num1, num2);
printGraph(graph);
} else if (strcmp(command, "del") == 0) {
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
removeEdge(graph, num1, num2);
printGraph(graph);
} else if (strcmp(command, "exit") == 0) {
break;
} else {
printf("Invalid command.\n");
}
}
freeGraph(graph);
return 0;
}